Help
About YPIBP
Construction of YPIBP
Usage of YPIBP
Motivation of YPIBP
Phosphoinositide or phosphatidylinositide (PI) or phosphatidylinositol phosphates is a family of lipids consists of the phosphorylated forms of phosphatidylinositol (PtdIns). They are profoundly involved in regulatory and intracellular signaling in eukaryotes. Proteins utilize their lipid-binding domains to interact with phosphatidylinositols to translocate to the specific membrane and gain functions. Yeast has been recognized as a eukaryotic model system to study lipid-protein interactions, and hundreds of yeast PI-binding proteins have been identified. Till now, this research knowledge remains scattered, and the complete PI-binding spectrum and potential lipid-binding domains enabling interaction could not be easily linked. To support lipid-protein interaction researchers working on the biology of phosphatidylinositols, there is no comprehensive tool available that can provide an interface to analyze the Protein-Domain-PI nexus.This prompts us to develop YPIBP (A repository for phosphoinositides-binding proteins in yeast) database.
What is YPIBP?
YPIBP is an inclusive database consisting of all the members of phosphatidylinositols-binding proteins which are collected from high-throughput proteome and lipid array studies, QuickGO and a rigorous literature mining. Cumulatively, across all PI, total of 679 PI-binding proteins were collected. YPIBP also contains protein domain information which is categorized as lipid-binding, lipid-related and others, helping users to underpin the domain-based knowledge on lipid-protein interactions.
Configuration of YPIBP database
The web interface of YPIBP was developed in Python using the Django MTV framework. The xx data were deposited in MySQL. All tables were produced by the JavaScript andfeature-rich JavaScript libraries (jQuery and DataTables) to present data on the webpage. The graphics (i.e. network figures) were generated by vis.js (a browser-based graphic drawing library).
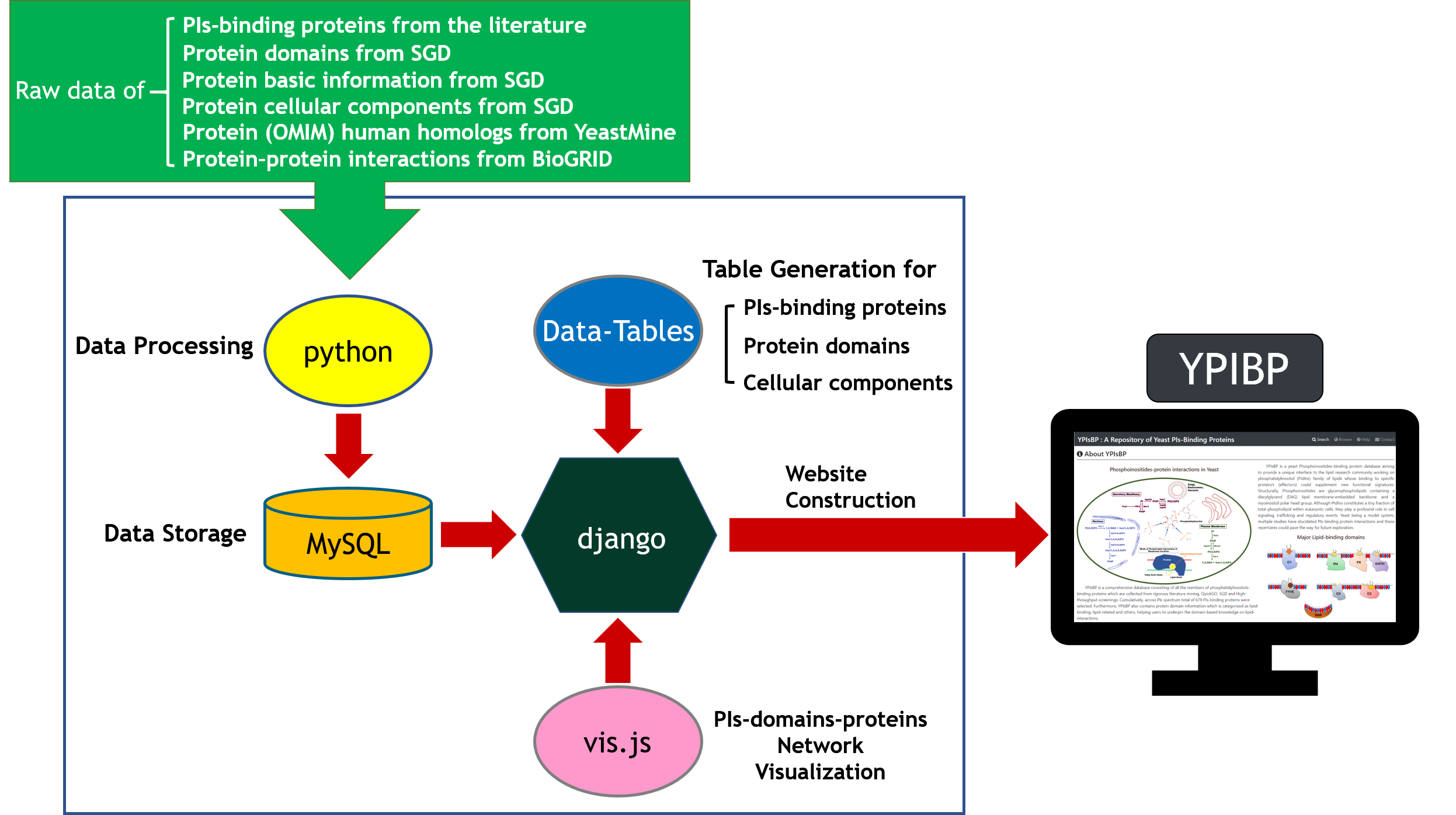
Collection of 679 lipid-binding proteins
We collected 8 sets of PI-binding yeast proteins which covers all members within PI. The first study by Zhu et al.(2001) provided the binding protein list for PI(3)P (51), PI(4)P (85), PI(3,4)P2 (71), PI(4,5)P2 (73) and PI(3,4,5)P3 (65), respectively [number in bracket represent total number of binding-proteins for a specific phosphatidylinositide]. Lu et al.(2012) provided a total of 295 P(3,5)P2 and 269 PtdIns-binding yeast proteins, respectively. Herianto et al. (2020) provided the 41 yeast PI(5)P-binding proteins which were also validated using flow-cytometry. Further, Gallego et al.(2010) used lipid array to define the selected proteins lipid-binding spectrum which resulted in PtdIns (32), PI(3)P (35), PI(4)P (48), PI(4,5)P2 (58) and PI(3,4,5)P3 (48) interactions, respectively.
QuickGO based Gene Ontology and GO Annotations terms derived list of proteins additionally complemented our comprehensive interaction data list.
We used total eight specific GO terms [e.g. Phosphatidylinositol-binding (GO:0035091), phosphatidylinositol-3-phosphate binding (GO:0032266), phosphatidylinositol-4-phosphate binding (GO:0070273), phosphatidylinositol-5-phosphate binding (GO:0010314), phosphatidylinositol-3,4-bisphosphate binding (GO:0043325), phosphatidylinositol-3,5-bisphosphate binding (GO:0080025), phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate binding (GO:0005546), phosphatidylinositol-3,4,5-Trisphosphate binding (GO:0005547)] to obtain proteins defined with a particular phosphatidylinositols-binding annotations. A collection of research articles was obtained by PubMed search engine.
A total 869 research articles were collected, after removing any redundancy, a total 203 papers were manually read and screened. Out of 203 papers total of 79 studies defined PI-binding properties using traditional and high-throughput methodologies(Supplementary the following table)
| Name of phosphoinositide | Keywords used | Number of paper(s) obtained from PubMed |
|---|---|---|
| PtdIns | "phosphatidylinositol-binding" "cerevisiae" | 7 |
| PI(3)P | "phosphatidylinositol 3 phosphate" "binding" "cerevisiae" | 72 |
| PI(4)P | "phosphatidylinositol 4 phosphate" "binding" "cerevisiae" | 58 |
| PI(5)P | "phosphatidylinositol 5 phosphate" "binding" "cerevisiae" | 1 |
| PI(3,4)P2 | "phosphatidylinositol 3,4 bisphosphate" "binding" "cerevisiae" | 2 |
| PI(3,5)P2 | "phosphatidylinositol 3,5 bisphosphate" "binding" "cerevisiae" | 15 |
| PI(4,5)P2 | "phosphatidylinositol 4,5 bisphosphate" "binding" "cerevisiae" | 56 |
| PI(3,4,5)P3 | "phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5 triphosphate" "binding" "cerevisiae" | 8 |
| PtdIns(3)P | "PtdIns(3)P" "binding" "cerevisiae" | 21 |
| PtdIns(4)P | "PtdIns(4)P" "binding" "cerevisiae" | 10 |
| PtdIns(5)P | "PtdIns(5)P" "binding" "cerevisiae" | 2 |
| PtdIns(3,4)P2 | "PtdIns(3,4)P2" "binding" "cerevisiae" | 1 |
| PtdIns(3,5)P2 | "PtdIns(3,5)P2" "binding" "cerevisiae"" | 8 |
| PtdIns(4,5)P2 | "PtdIns(4,5)P2" "binding" "cerevisiae" | 11 |
| PtdIns(3,4,5)P3 | "PtdIns(3,4,5)P3" "binding" "cerevisiae" | 8 |
| PtdIns | “PtdIns” "binding" "cerevisiae" | 80 |
| Phosphatidylinositol (common) | "phosphatidylinositol” “binding" "cerevisiae" | 509 |
Collection of lipid-binding domains and lipid-related domains
A complete list of yeast protein domains was obtained using the SGD and YeastMine database consisting of the proteome-wide collection of identified domains present in every protein of yeast. Based on the description of the lipid-binding domain by Chiapparino et al.(2016), DiNitto et al.(2003) and Stahelin et al.(2009) . Further, to define lipid-related domains, we utilized the inclusion of specific terms such as “lipid” and other unique lipid names such as “Phosphatidylserine”, “Phosphatidylinositol”, “Sterol” etc. to categorize them as lipid-related domains. The rest of the domains were categorized as “Others”.
Testing the enrichment of input genes
Testing the enrichment of the binding proteins of 8 PI in the input genes
For users' input genes, YPIBP tests whether they are enriched with the proteins which bind to the specific phosphoinositide under study. The p-value is calculated using hypergeometric test as follows.
$$P_{value} = \sum^{min(A,I)}_{x=K} \frac{\left(\begin{matrix}A\\x\end{matrix} \right)\left(\begin{matrix}G-A\\I-x\end{matrix}\right)}{\left(\begin{matrix}G\\I\end{matrix}\right)}$$
where G=6705 is the number of yeast genes which have protein products, A is the number of proteins which binding the specific phosphoinositide of insterest(e.g. A = 240 for PtdIns, A = 107 for PI(3,4)P2, etc.), I is the number of users’ input genes, and K is the number of input protein which bind to the specific phosphoinositide under study.
Testing the enrichment of the protein domains the input genes
For users' input genes, YPIBP tests whether they are enriched with any protein domains. The p-value is calculated using hypergeometric test as follows.
$$P_{value} = \sum^{min(A,I)}_{x=K} \frac{\left(\begin{matrix}A\\x\end{matrix} \right)\left(\begin{matrix}G-A\\I-x\end{matrix}\right)}{\left(\begin{matrix}G\\I\end{matrix}\right)}$$
where G=6705 is the number of yeast genes which have protein products, A is the number of proteins which have the protein domain of interest(e.g. A = 8 for SM00273, A = 40 for G3DSA:2.30.29.30, etc.), I is the number of users’ input genes, and K is the number of input protein which have the protein domain of interest.
Evidence code explanations
| Evidence code | Explanations |
|---|---|
| HDA | Inferred from High Throughput Direct Assay |
| IDA | Inferred from Direct Assay |
| IPI | Inferred from Physical Interaction |
| IBA | Inferred from Biological aspect of Ancestor |
| IMP | Inferred from Mutant Phenotype |
| IEA | Inferred from Electronic Annotation |
| IGI | Inferred from Genetic Interaction |
| IKR | Inferred from Key Residues |
| ISS | Inferred from Sequence or structural Similarity |
| EXP | Inferred from Experiment |
| TAS | Traceable Author Statement |
| RCA | Inferred from Reviewed Computational Analysis |
Database interface
YPIBP provides two search modes
First search mode:
Users can input a protein name (systematic, standard, or alias name).
After submitting a single input protein, YPIBP yields an output page with results in four compartments. The first section showed the basic information such as systematic name, standard name, aliases and description of the input protein and link to SGD to see the additional characterization of protein of interest in the yeast system. Further, we also provide human homolog including OMIM human homolog representative disease phenotype(s).
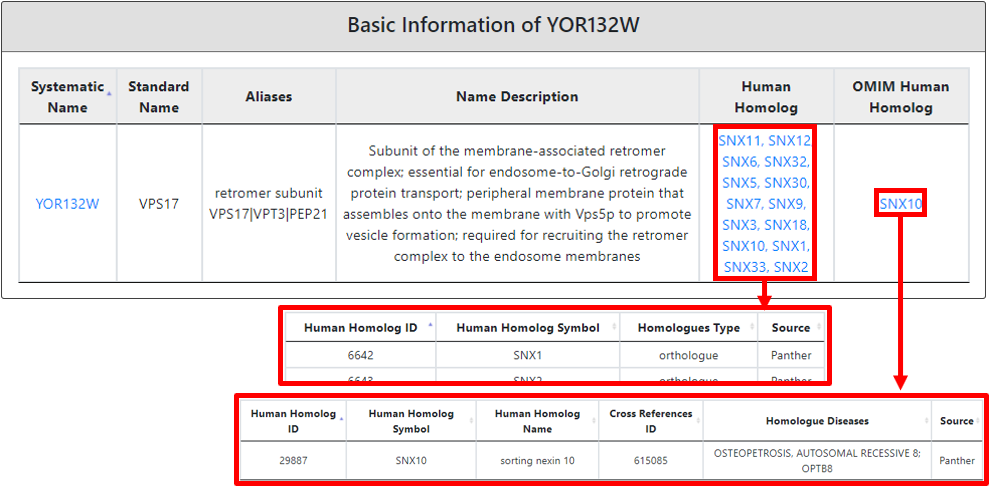
If the input protein is any of the PI-binding protein defined by YPIBP, the details regarding its PI-binding spectrum is provided with a total number of evidence(s) for each phosphatidylinositide-binding attribute.
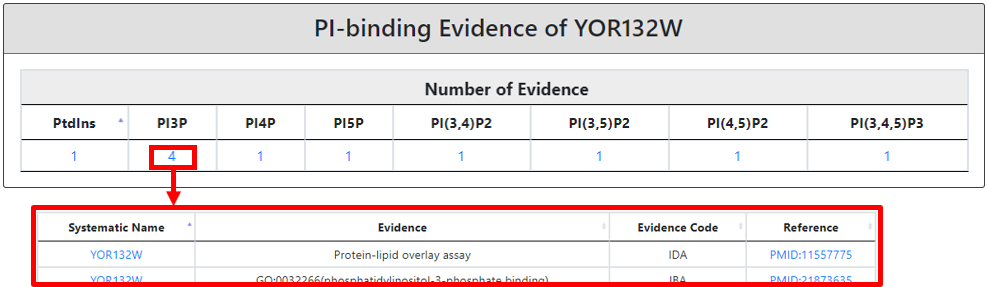
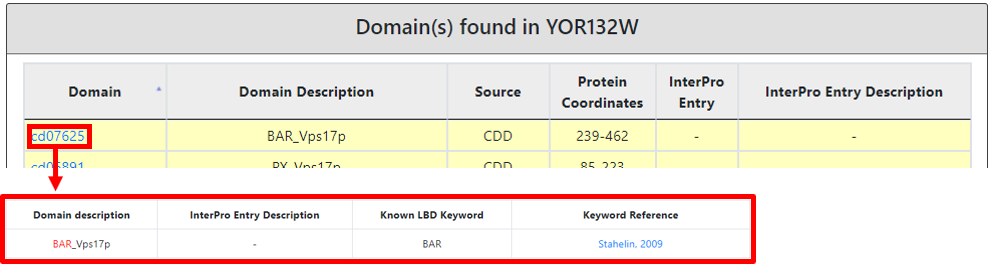
Moreover, in the third section, we also provide the categorized (color-coded) description of lipid-binding (highlighted in yellow), lipid-related (highlighted in green) and other domains present in the protein of interest. Each domain is mentioned with its name, description, source of nomenclature, protein coordinates, InterPro entry (hyperlinked to InterPro) and InterPro entry description. A lipid-binding domain name is hyperlinked to a new page explaining in a detailed connection to a well-known lipid-binding domain type with a reference. And based on the literature linked most probable lipid-binding lipid(s) spectrum detail.
In the fourth section, we provided the cellular component information which allow user to identify specific organelle or compartment where the protein is located.

Second search mode:
Users can input a list of genes.
First, based on the binding evidence(s) matching, we have provided a table of PI-binding spectrum showing each PI-specific binding evidence(s)
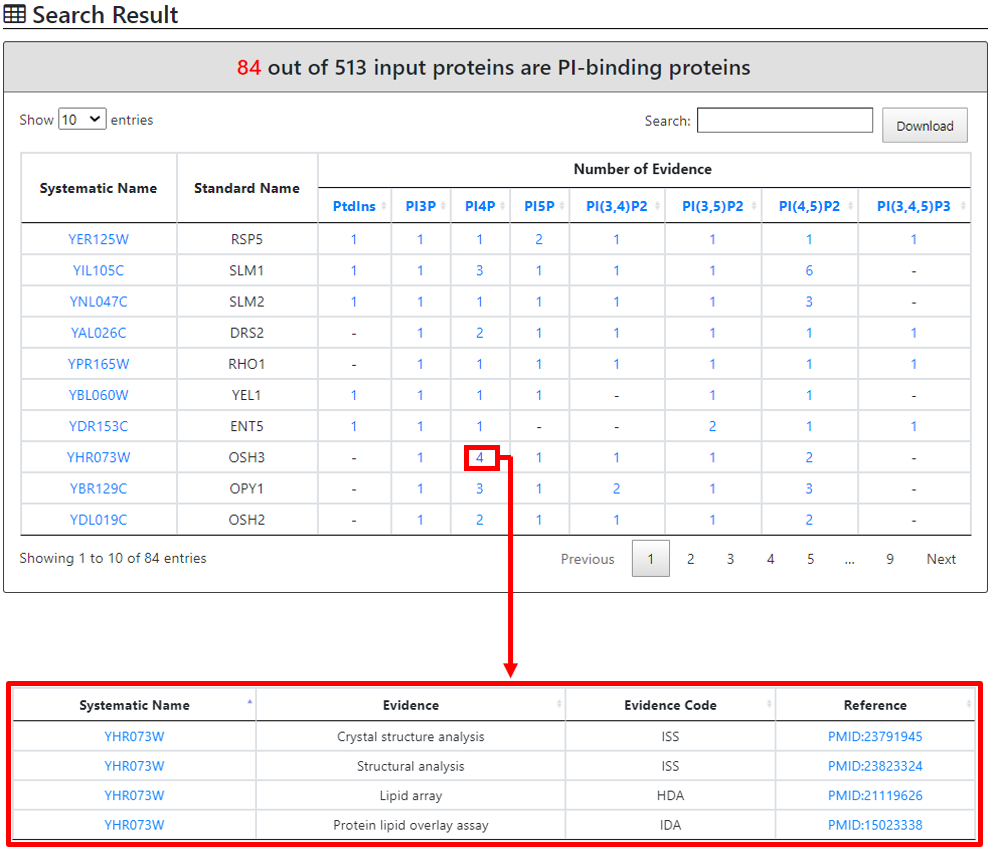
Subsequently, an enriched PI-binding will be showcased in the table format along with domain enrichment analysis as the output page. The output page will also provide the user with the expected value for a specific proportion of proteome wide-PI-binding proteins and the input derived real value proportion along with the P-value. The real value protein number which supports the enrichment is linked to the respective table, listing their systematic and standard names along with an intrinsic link showing a specific protein PI-binding characteristic within our database.
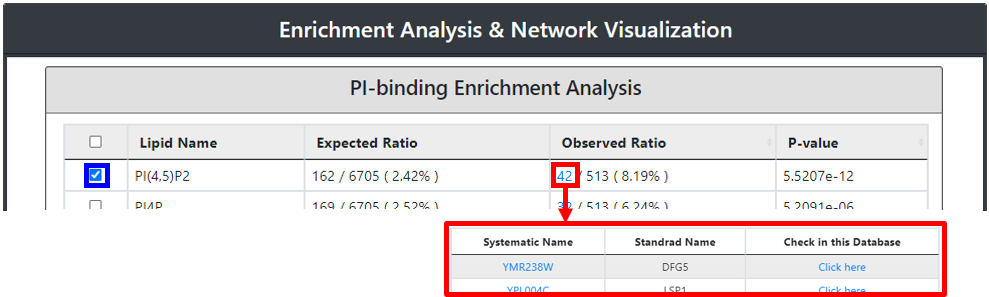
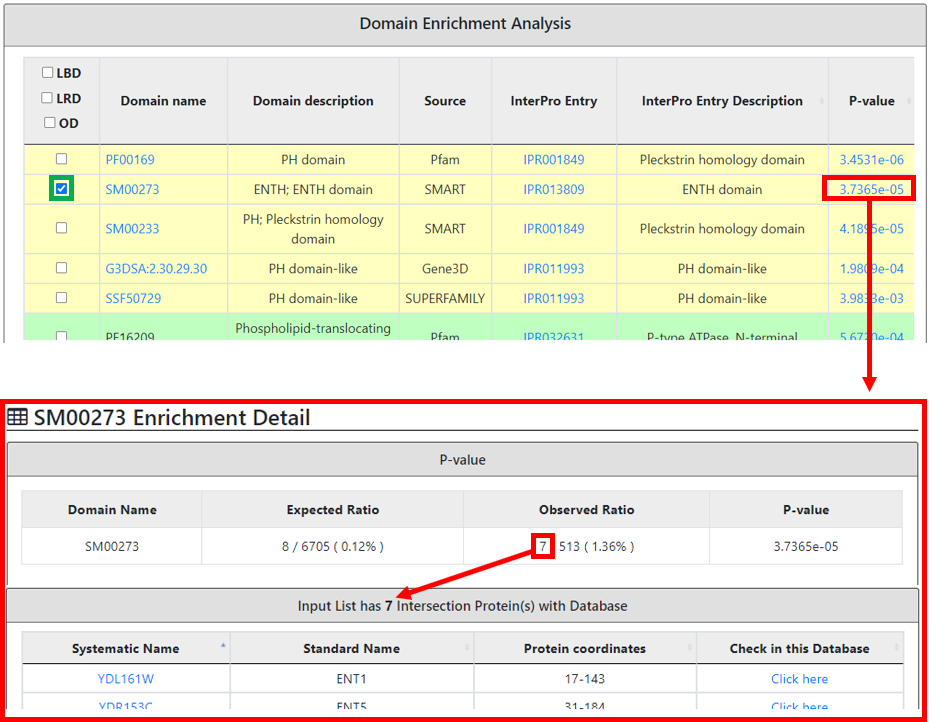
The domain enrichment analysis is categorized as explained earlier with additional details showing its enrichment P-value. The P-value link provides the expected, real as well as calculated P-value at specific tests such as FDR or Bonferroni or none used at particular P-value cut-off. Moreover, this P-value page also provides a table with the list of protein(s) names containing this specific domain, its protein coordinates and an individual protein internal link.
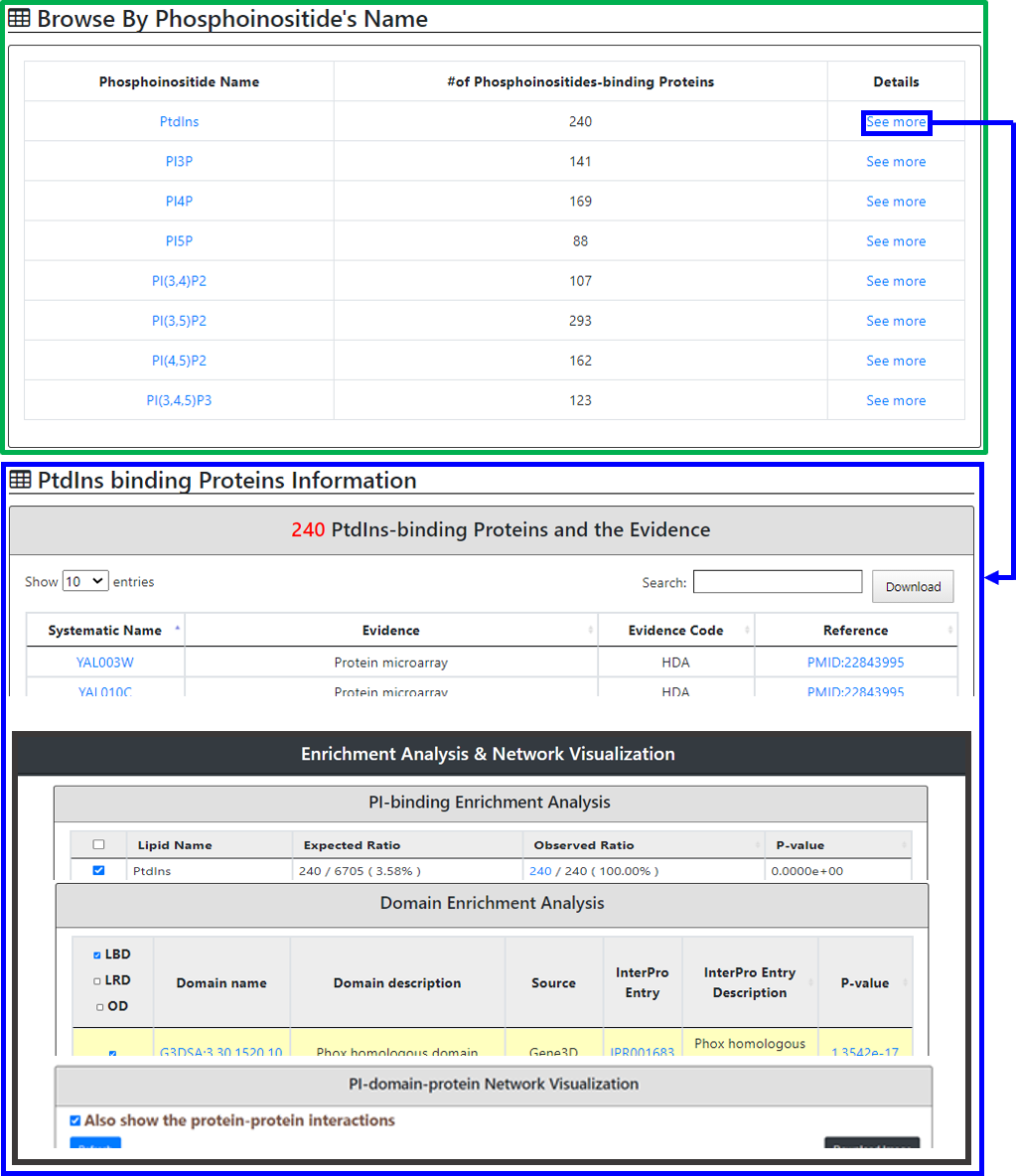
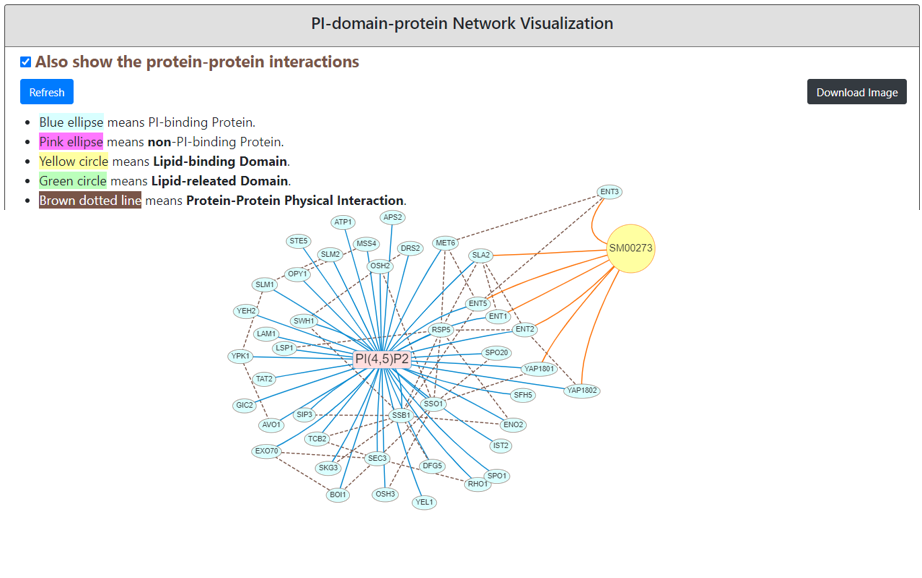
Selected phosphatidylinositol (PtdIns)’s binding proteins information and their enrichment test with protein-domain-phosphatidylinositol network visualization
YPIBP provides two browse modes
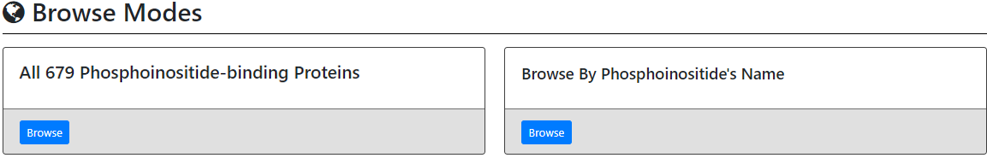
First browse mode:
Users can go through all 679 phosphatidylinositols-binding proteins in table format. For each protein, YPIBP provides a systematic name, a standard name and specific PI-binding evidences
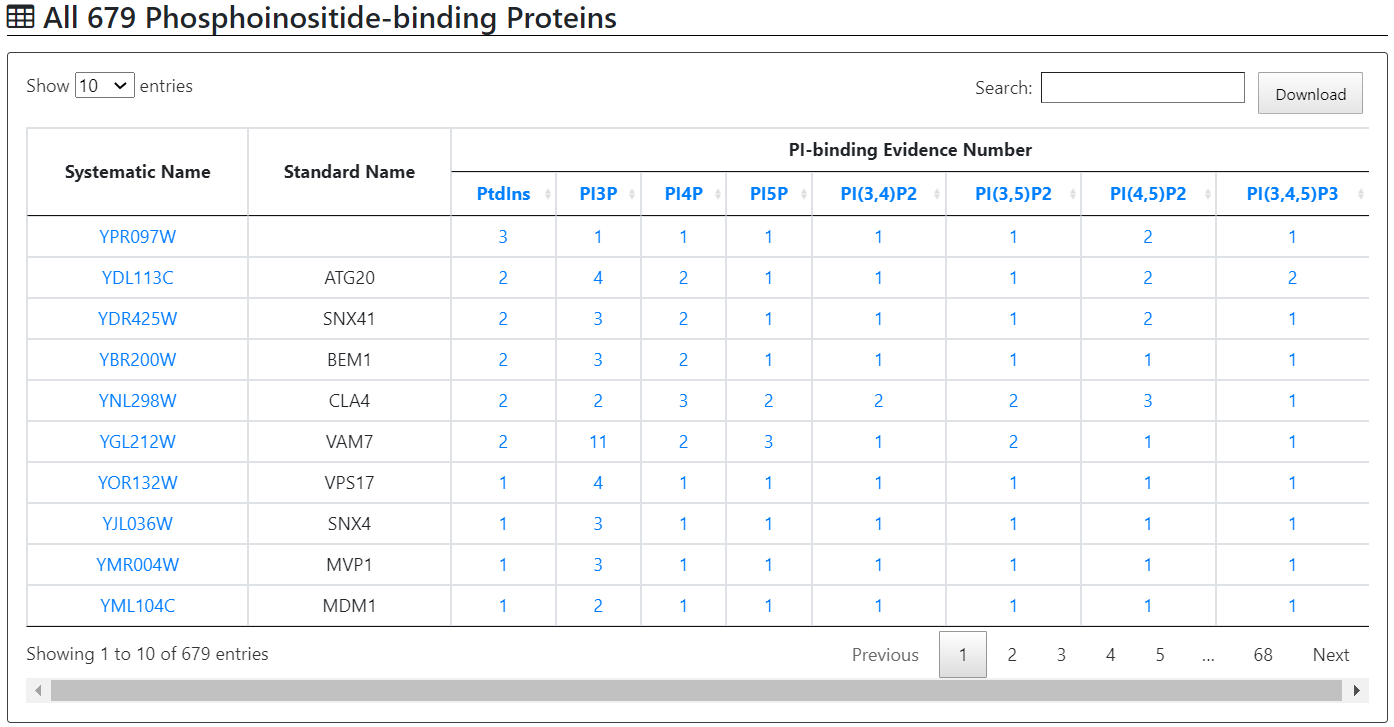
Second browse mode:
Users can browse all eight PI and the total number of yeast proteins with a PtdIns-binding is mentioned. In the details, a table showing the systematic name of the protein, evidence, evidence code and its reference [linked to PubMed ID (PMID)] is provided along with its enrichment and visualization .